
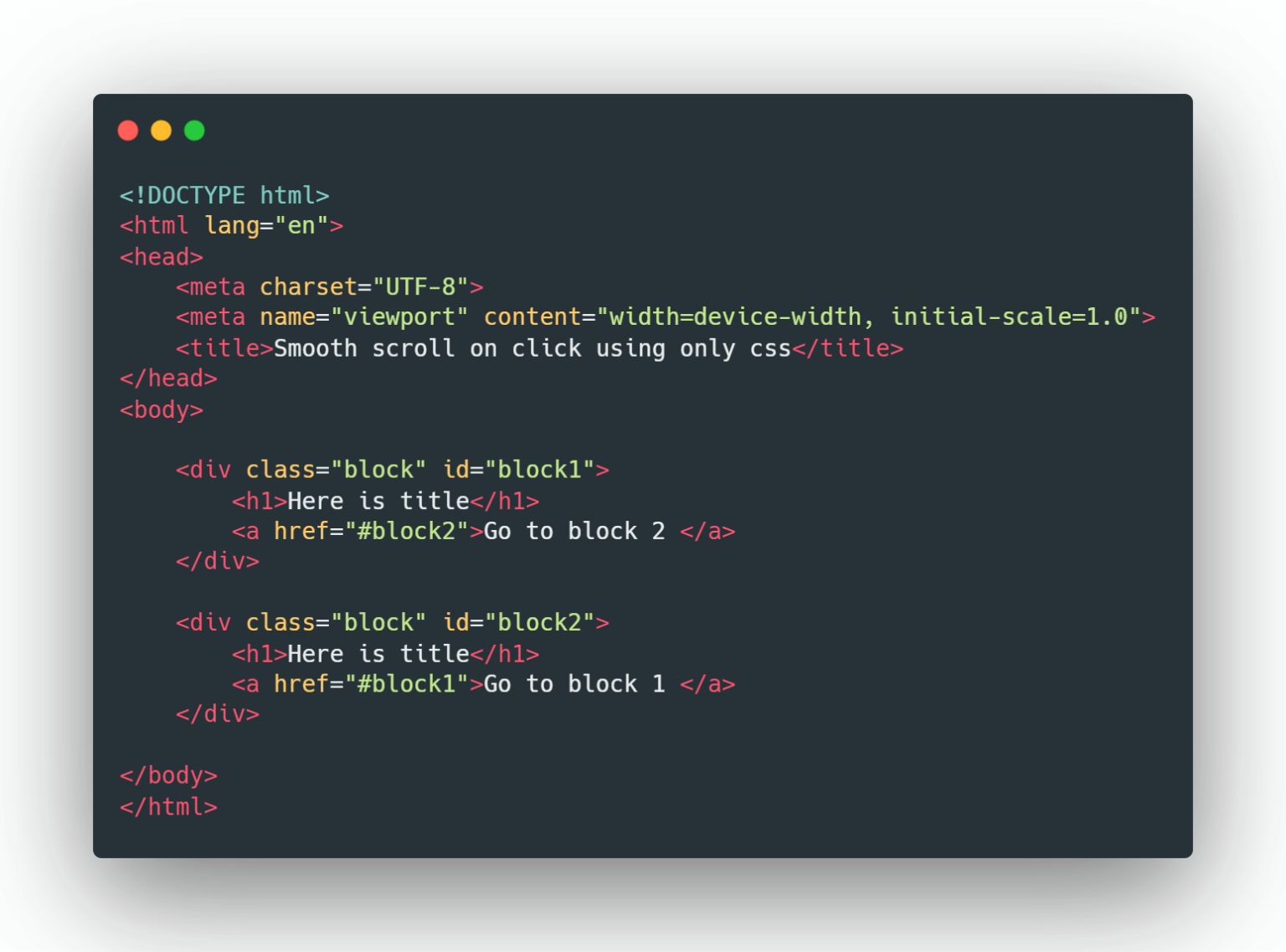
I made a PR to slightly improve the docs, you might find the code easier to understand with it. If you have more curiosity, I highly suggest studying the polyfill's source code, it's less than 500 lines in total. It does not support smooth scrolling by setting scrollLeft/ scrollTop and it does not support the scrollIntoView() options (it always aligns the element at the top). It polyfills scroll(), scrollTo(), scrollBy(), scrollIntoView() and the CSS scroll-behavior. If you need more reassurance, there's a very good smooth scroll polyfill that I use in my projects. scrollTo ( As of this writing, all major browsers – except Safari – support smooth scroll and the scrolling methods described in this article. There's also a new signature for this method, which uses an object instead of two numeric arguments, and with this new signature, we can explicitly set our scroll behavior. You simply call element.scrollTo(x, y) and it'll respect the CSS scroll-behavior of the element. If you have the x and y coordinates for where you want to scroll the user to, you can simply call window.scrollTo(x, y) and it'll respect the CSS scroll-behavior of the page. This method is ideal for scrolling to absolute coordinates. Link Window.scrollTo() and Element.scrollTo() In practice, you can use either, just choose one and be consistent. To avoid duplicate content, I'll just refer to scrollTo(). That's because Window.scroll() and Element.scroll() are effectively the same methods as Window.scrollTo() and Element.scrollTo(). Maybe you've noticed that I haven't mentioned the scroll() method.
Link (Note) Window.scroll() and Element.scroll() We'll explore these methods individually. User agents should follow platform conventions, if any. Ğlement.scrollTop = y JavaScript - Window. The scrolling box scrolls in a smooth fashion using a user-agent-defined timing function over a user-agent-defined period of time. Some ways of programmatically triggering a scroll event are through: - Window.scrollTo() I say "programmatically triggered" because it's not going to smooth scroll the mouse wheel. scroll-behavior: smooth applies a smooth transition when a scroll event is programmatically triggered.scroll-behavior: instant is the same as auto, which is why it was deprecated. Method of specifying the scrolling behavior for a scrolling box, when scrolling happens due to navigation or CSSOM scrolling APIs.scroll-behavior: auto is the default instant scrolling behavior that we're already used to.The CSS scroll-behavior property accepts one of three values – or two, actually, since one of those was deprecated. Let me introduce you to our tools for a native smooth scroll. Menu Table of Contents CSS scroll-behavior (Note) Window.scroll() and Element.scroll() Window.scrollTo() and Element.scrollTo() Element.scrollLeft and Element.scrollTop (Note) Negative Element.scrollLeft Window.scrollBy() and Element.scrollBy() (Note) Window.scrollByLines() and Window.scrollByPages() Element.scrollIntoView() Browser Support CTA Referencesĭo you want a smooth scroll? Forget JQuery, we're past that.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
